The relationship between what we eat and how our bodies process sugar has never been more critical to understand. As rates of type 2 diabetes continue climbing worldwide, researchers are uncovering fascinating connections between our digestive health and blood sugar control. The emerging science of Diabetes & Gut Health reveals that the trillions of microorganisms living in our intestines play a pivotal role in insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism, and overall metabolic wellness.
Your gut microbiome—the complex ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms residing in your digestive tract—acts as a powerful regulator of blood sugar levels. This intricate relationship between Diabetes & Gut Health suggests that supporting your digestive system through targeted nutrition may be one of the most effective strategies for preventing and managing insulin resistance. Understanding this connection opens up exciting possibilities for natural approaches to blood sugar management that go far beyond simply counting carbohydrates.
Modern research is revealing that individuals with type 2 diabetes often have distinctly different gut bacterial compositions compared to metabolically healthy people. This discovery has sparked intense scientific interest in how we can leverage nutrition to cultivate beneficial gut bacteria while reducing harmful strains that contribute to insulin resistance and inflammation.
What Is the Diabetes & Gut Health Connection and Why It Matters?
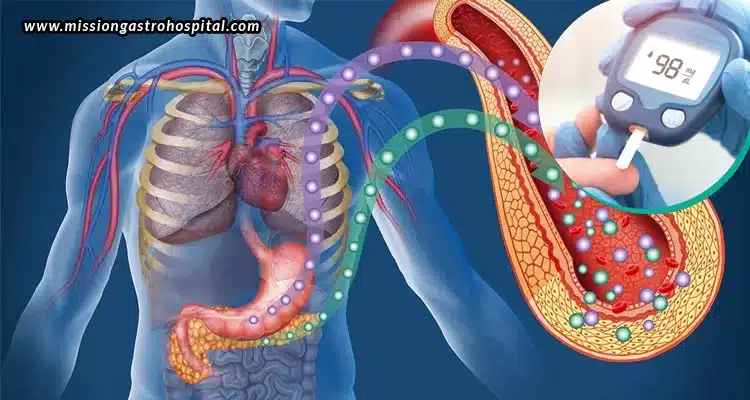
The Diabetes & Gut Health relationship centers on how your gut microbiota influences glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity throughout your body. Your intestinal bacteria produce various compounds called metabolites that can either enhance or impair your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar effectively. When beneficial bacteria thrive, they produce short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
Conversely, an imbalanced gut microbiome—a condition called dysbiosis—can contribute to increased intestinal permeability, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance. Harmful bacteria may produce endotoxins that trigger inflammatory responses, making it harder for your cells to respond properly to insulin signals. This creates a vicious cycle where poor blood sugar control further disrupts gut bacterial balance.
The gut-brain-pancreas axis represents another crucial aspect of this relationship. Your gut bacteria communicate with your brain and pancreas through various pathways, including the vagus nerve and hormone signaling. This communication network influences insulin production, glucose tolerance, and even food cravings that can impact blood sugar stability.
Research shows that people with diverse, healthy gut microbiomes tend to have better glucose control and lower inflammation markers. This suggests that cultivating beneficial bacteria through targeted nutrition could serve as a powerful tool for both preventing and managing diabetes naturally.
Health Benefits of Supporting Diabetes & Gut Health
Optimizing the Diabetes & Gut Health connection through proper nutrition offers numerous metabolic benefits beyond simple blood sugar control. A healthy gut microbiome enhances the production of beneficial metabolites that directly improve insulin sensitivity at the cellular level. These compounds help your muscles and organs utilize glucose more efficiently, reducing the burden on your pancreas to produce excessive insulin.
Improved gut barrier function represents another significant benefit. When beneficial bacteria dominate your microbiome, they strengthen the intestinal lining, reducing the passage of inflammatory compounds into your bloodstream. This enhanced barrier function helps break the cycle of chronic inflammation that contributes to insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.
Weight management becomes more achievable when your gut health is optimized. Certain beneficial bacteria influence hormones like GLP-1 and peptide YY, which regulate satiety and reduce food cravings. A balanced microbiome also affects how efficiently your body extracts calories from food and stores fat, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight that supports blood sugar control.
The anti-inflammatory effects of a healthy gut microbiome extend throughout your entire body. Reduced systemic inflammation improves cardiovascular health, brain function, and immune system regulation—all crucial factors for long-term diabetes prevention and management. Many people report increased energy levels, better mood stability, and improved sleep quality when their gut health improves.
Enhanced nutrient absorption represents an often-overlooked benefit. A healthy gut microbiome improves your body’s ability to extract and utilize vitamins, minerals, and other compounds essential for optimal glucose metabolism. This includes better absorption of magnesium, chromium, and B-vitamins that directly support healthy blood sugar levels.
Challenges and Practical Solutions for Gut Health Optimization
Supporting Diabetes & Gut Health through nutrition presents several challenges that require thoughtful strategies to overcome. The modern Western diet, high in processed foods and low in fiber, actively promotes harmful bacterial growth while starving beneficial microorganisms. Transitioning to a gut-friendly eating pattern requires significant dietary changes that can feel overwhelming initially.
Antibiotic use, while sometimes necessary for health, can dramatically disrupt gut bacterial balance. Even a single course of antibiotics can reduce beneficial bacteria for months or years. If antibiotics are unavoidable, implementing a comprehensive gut restoration protocol becomes essential for maintaining metabolic health.
Individual variation in gut microbiome composition means that foods beneficial for one person might not provide the same benefits for another. This personalized aspect of gut health requires patience and experimentation to identify which foods and supplements work best for your unique bacterial ecosystem.
Stress, poor sleep, and sedentary lifestyles all negatively impact gut health and blood sugar control simultaneously. Addressing these lifestyle factors becomes crucial for optimizing the Diabetes & Gut Health connection. Implementing stress management techniques, prioritizing quality sleep, and incorporating regular physical activity all support both gut bacterial balance and glucose metabolism.
The time required to see significant improvements in gut health can test patience. While some people notice changes within weeks, meaningful shifts in gut bacterial composition typically take 2-6 months of consistent dietary and lifestyle changes. Understanding this timeline helps maintain motivation during the initial phases of gut health optimization.
biotics. Store components separately for up to 3 days and assemble just before eating to maintain optimal texture and probiotic viability.
Current Trends in Gut Health and Diabetes Management

The intersection of Diabetes & Gut Health continues evolving with exciting developments in personalized medicine and functional nutrition. Microbiome testing has become increasingly accessible, allowing individuals to identify specific bacterial imbalances and tailor their dietary interventions accordingly. These tests can reveal which beneficial bacteria are lacking and which harmful strains may be overrepresented.
Continuous glucose monitoring paired with food tracking apps enables real-time assessment of how different foods affect both blood sugar and digestive comfort. This technology helps people understand their personal responses to various gut-supporting foods and optimize their choices for both metabolic and digestive health.
Targeted probiotic supplementation based on individual needs represents a growing trend. Rather than taking generic probiotic blends, practitioners increasingly recommend specific bacterial strains shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Strains like Akkermansia muciniphila and certain Lactobacillus species show particular promise for diabetes management.
The concept of “psychobiotics”—probiotics that influence mood and brain function—is gaining recognition for its role in diabetes management. Since stress and mood significantly impact blood sugar control, supporting gut bacteria that produce mood-stabilizing compounds like GABA and serotonin offers a holistic approach to metabolic health.
Fermented food diversity is expanding beyond traditional options like yogurt and sauerkraut. People are exploring kefir, kombucha, tempeh, miso, and other cultured foods to diversify their probiotic intake and support broader gut bacterial diversity essential for optimal glucose metabolism.
Frequently Asked Questions

Question: How long does it take to see improvements in blood sugar after focusing on gut health?
Answer: Most people begin noticing digestive improvements within 1-2 weeks, but significant changes in blood sugar control typically occur after 6-12 weeks of consistent gut-supporting nutrition. Individual responses vary based on starting gut health status and adherence to dietary changes.
Question: Can probiotics alone improve diabetes management without dietary changes?
Answer: While targeted probiotics can provide benefits, they work best when combined with a gut-supporting diet rich in prebiotic fibers. The combination of beneficial bacteria (probiotics) and their preferred food sources (prebiotics) creates the most effective environment for improving glucose metabolism.
Question: Are there specific foods I should avoid to protect my gut health if I have diabetes?
Answer: Highly processed foods, artificial sweeteners, excessive sugar, and foods high in advanced glycation end products (AGEs) can disrupt gut bacterial balance. Focus on reducing ultra-processed foods while increasing whole foods, fermented vegetables, and fiber-rich options for optimal gut and blood sugar health.
Question: How do I know if my gut health is improving while managing diabetes?
Answer: Positive signs include more stable blood sugar readings, improved digestion, better sleep quality, increased energy levels, and reduced cravings for sugary foods. Many people also experience better mood stability and decreased inflammation markers as their gut health improves.
Question: Can gut health interventions replace diabetes medications?
Answer: Gut health optimization should complement, not replace, prescribed diabetes medications without medical supervision. Work with your healthcare provider to monitor blood sugar improvements as gut health strategies may allow for medication adjustments over time, but never discontinue prescribed treatments independently.
Conclusion

The powerful connection between Diabetes & Gut Health offers hope and practical strategies for anyone seeking to improve their blood sugar control naturally. By understanding how your gut microbiome influences glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation, you can make informed dietary choices that support both digestive wellness and metabolic health simultaneously.
Supporting your gut health through targeted nutrition isn’t just about managing current blood sugar levels—it’s an investment in long-term metabolic wellness that can help prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life. The strategies we’ve explored, from incorporating prebiotic-rich foods to optimizing gut bacterial diversity, provide a foundation for sustainable diabetes management that works with your body’s natural systems.
Ready to explore more evidence-based approaches to natural blood sugar management? Visit sugardetoxlab.com for additional gut-healthy recipes, comprehensive guides to functional nutrition, and practical tips for optimizing your metabolic health. Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest research updates on the Diabetes & Gut Health connection and start your journey toward better blood sugar control through digestive wellness today.